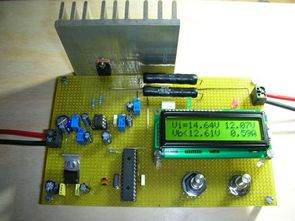
With the charging circuit, lion lipo life, lead batteries can be charged, and it has been stated that NiCad and NiMh batteries can be charged slowly without delta (google translate) The charging circuit is controlled with pic16f876, charging, battery voltage and current information are displayed on a 2×16 lcd.
Since mosfet (irfz44) is used as a power transistor, its power is high (0-5a) Supply voltage: 6 for 20V Current: 20mA – 5a Output: 20mV – 20V 0
Software prepared with micro c source C, hex and other codes schema (+ orcad) files are available
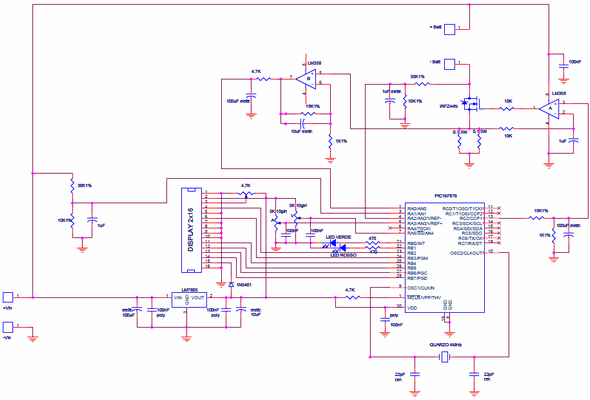
The circuit in question is halfway between a power supply and a battery charger.
It was born from the need to have something very versatile, so as not to be cut off if a new type of battery becomes available, the reference is to the new LiFe A123 cells.
In detail, the circuit is able to function as a constant current generator but with a variable voltage clamp at will. It is simply equipped with 2 10-turn potentiometers, a 2×16 character display and 2 LEDs, no buttons are present.
Rating plate data:
Supply voltage: from 6 to 20V;
Current: from 0 to 5A, in 20mA steps;
Voltage: from 0 to 20V, in 20mV steps;
data on the display: input voltage, battery voltage, clamp voltage, output current.
2 LEDs: red for the CC phase, green for the CV phase.
The difference compared to a laboratory power supply is that the Batt-Power is designed for charging cells with a CC/CV algorithm, i.e. constant current-constant voltage, because in the meantime the current grows softly, avoiding possible unpleasant problems.
It can also be used in the field, powering it at 12V, even if at the moment it can charge batteries with voltage <12V, but as we will see it has some other interesting non-conventional uses. But which and how many cells can it charge?
It charges Lead-gel, LiIon, LiPo and LiFe (A123).
It also charges NiCad and NiMh, but without the delta-peak, so either slow charging at 1/10C or for example at 1C but using an external thermometer on the pack and manually disconnecting the current.
With 12V power supply it can charge up to 3 Pb cells (6V), 2 LiPo cells (7.4V) and 3 A123 cells, the main use for which it was designed.
Used with a power supply capable of providing 20V (max.) and more than 5 amps it can charge much larger packs, I’ll leave the calculation of the number of cells to you, I’ll just point out that the circuit is able to function until the pack voltage is lower than the supply voltage of 200mV, so the input voltage is well exploitable.
What the circuit doesn’t have is the measurement of the charge (in mAh) and the time, but it is not in fact a traditional charger, let’s say it is designed for geeks who want maximum freedom.
Those who want to know other data can always insert one of those tools such as Watt’s UP, capable of detecting the charge, between the output and the pack to be charged.
What else does it do?
If you want, you can discharge a given pack at constant current, just connect the aforementioned to the input this time and short-circuit the output tips or better connect a load, such as a power resistor or a battery with fewer cells and/or lower voltage.
Another possible thing is, for example, to test the spark plugs of our glow engines (if not even power them during starting…): it is possible to know the working point of a given spark plug, that is, the optimal current and voltage.
Source: baronerosso.net alternative link:
Şifre-Pass: 320volt.com
Publication date: 2011/05/29 Tags: battery charger circuit, microchip projects, microcontroller projects, pic16f876 projects
Atmel Development Board ATmega16 ATmega32
Experiment card design, layout and ATmega32 microcontroller ATMega16 been quite well prepared for the software can be tested not very advanced test card may be enough for a lot of users.
Try some of the features of the Atmel Development Board; 4-digit LED display, WA replicated; 4 × 4 or 4 × 1 keypad (buttons), Buzz Real Time Clock PCF8583;, 2 × 16 LCD, Converters D / potentiometer, TSOP1736 IR receiver, IR LED transmitter 24Cxx Memory Place Serial EEPROM ULN2003 CMOS compatible TTL TWI interface connector JTAG programming RS232 connection ATMega16